short run supply curve formula
Derive the firms supply curve from the firms marginal cost curve and the industry supply curve from the supply curves of individual firms. 
 Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA), Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA), Capital Markets & Securities Analyst (CMSA), Certified Business Intelligence & Data Analyst (BIDA), Financial Planning & Wealth Management (FPWM). When the price level changes and firms produce more in response to that, we move along the SRAS curve. Notice that a line drawn tangent to the total cost curve at that quantity has the same slope as the total revenue curve. 8 shows that at a price of Rs. The SRAS curve tells us that firms will respond to inflation by producing more. the dollar amount that the firm earns from sales of its output. It is usually an upward-sloping curve as the relationship between price increases is directly proportional to the rise in output levels. We will use this cell as the correct optimal solution in all cases, including the shutdown case. In this case, assume that a = : $2 billion. Building confidence in your accounting skills is easy with CFI courses! If price falls below average variable cost, the firm will shut down in the short run, reducing output to zero. The short-run final domestic supply is driven by price. Because the price of $0.10 falls below his average variable cost, his best course would be to shut down. Therefore, Mr. Gortari should continue to produce an output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue. As the new Iridium became unburdened from the debt of the old one and technology improved, the lower fixed and variable costs have contributed to Iridiums revival, but clearly a critical element in the turnaround has been increased demand. Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue. 2.3 Applications of the Production Possibilities Model, 4.2 Government Intervention in Market Prices: Price Floors and Price Ceilings, 5.2 Responsiveness of Demand to Other Factors, 7.3 Indifference Curve Analysis: An Alternative Approach to Understanding Consumer Choice, 8.1 Production Choices and Costs: The Short Run, 8.2 Production Choices and Costs: The Long Run, 9.2 Output Determination in the Short Run, 11.1 Monopolistic Competition: Competition Among Many, 11.2 Oligopoly: Competition Among the Few, 11.3 Extensions of Imperfect Competition: Advertising and Price Discrimination, 14.1 Price-Setting Buyers: The Case of Monopsony, 15.1 The Role of Government in a Market Economy, 16.1 Antitrust Laws and Their Interpretation, 16.2 Antitrust and Competitiveness in a Global Economy, 16.3 Regulation: Protecting People from the Market, 18.1 Maximizing the Net Benefits of Pollution, 20.1 Growth of Real GDP and Business Cycles, 22.2 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply: The Long Run and the Short Run, 22.3 Recessionary and Inflationary Gaps and Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium, 23.2 Growth and the Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve, 24.2 The Banking System and Money Creation, 25.1 The Bond and Foreign Exchange Markets, 25.2 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium in the Money Market, 26.1 Monetary Policy in the United States, 26.2 Problems and Controversies of Monetary Policy, 26.3 Monetary Policy and the Equation of Exchange, 27.2 The Use of Fiscal Policy to Stabilize the Economy, 28.1 Determining the Level of Consumption, 28.3 Aggregate Expenditures and Aggregate Demand, 30.1 The International Sector: An Introduction, 31.2 Explaining InflationUnemployment Relationships, 31.3 Inflation and Unemployment in the Long Run, 32.1 The Great Depression and Keynesian Economics, 32.2 Keynesian Economics in the 1960s and 1970s, 32.3. The short-run individual supply curve is the individuals marginal cost at all points greater than the minimum average variable cost. In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to short-run aggregate supply. and any corresponding bookmarks? To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. The short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) lets us capture how all of the firms in an economy respond to price stickiness. the idea that firms might not change their prices when there is a change in the price level because it is costly to do so; menu costs have been proposed as one of the reasons that prices are sticky in an economy. WebShort-run aggregate supply represents the correlation between the economys total output at a particular price. Suppose that his total fixed cost is $400 per month. When the marginal value exceeds the average value, the average value will be rising. Movements along the SRPC correspond to shifts in aggregate demand, while shifts of the entire SRPC correspond to shifts of the SRAS (short-run aggregate supply) curve. When producing 4,444 pounds of radishes per month, Mr. Gortari faces an average total cost of $0.23 per pound. Today, most economists believe that prices are sticky (at least in the short run).
Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA), Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA), Capital Markets & Securities Analyst (CMSA), Certified Business Intelligence & Data Analyst (BIDA), Financial Planning & Wealth Management (FPWM). When the price level changes and firms produce more in response to that, we move along the SRAS curve. Notice that a line drawn tangent to the total cost curve at that quantity has the same slope as the total revenue curve. 8 shows that at a price of Rs. The SRAS curve tells us that firms will respond to inflation by producing more. the dollar amount that the firm earns from sales of its output. It is usually an upward-sloping curve as the relationship between price increases is directly proportional to the rise in output levels. We will use this cell as the correct optimal solution in all cases, including the shutdown case. In this case, assume that a = : $2 billion. Building confidence in your accounting skills is easy with CFI courses! If price falls below average variable cost, the firm will shut down in the short run, reducing output to zero. The short-run final domestic supply is driven by price. Because the price of $0.10 falls below his average variable cost, his best course would be to shut down. Therefore, Mr. Gortari should continue to produce an output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue. As the new Iridium became unburdened from the debt of the old one and technology improved, the lower fixed and variable costs have contributed to Iridiums revival, but clearly a critical element in the turnaround has been increased demand. Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue. 2.3 Applications of the Production Possibilities Model, 4.2 Government Intervention in Market Prices: Price Floors and Price Ceilings, 5.2 Responsiveness of Demand to Other Factors, 7.3 Indifference Curve Analysis: An Alternative Approach to Understanding Consumer Choice, 8.1 Production Choices and Costs: The Short Run, 8.2 Production Choices and Costs: The Long Run, 9.2 Output Determination in the Short Run, 11.1 Monopolistic Competition: Competition Among Many, 11.2 Oligopoly: Competition Among the Few, 11.3 Extensions of Imperfect Competition: Advertising and Price Discrimination, 14.1 Price-Setting Buyers: The Case of Monopsony, 15.1 The Role of Government in a Market Economy, 16.1 Antitrust Laws and Their Interpretation, 16.2 Antitrust and Competitiveness in a Global Economy, 16.3 Regulation: Protecting People from the Market, 18.1 Maximizing the Net Benefits of Pollution, 20.1 Growth of Real GDP and Business Cycles, 22.2 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply: The Long Run and the Short Run, 22.3 Recessionary and Inflationary Gaps and Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium, 23.2 Growth and the Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve, 24.2 The Banking System and Money Creation, 25.1 The Bond and Foreign Exchange Markets, 25.2 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium in the Money Market, 26.1 Monetary Policy in the United States, 26.2 Problems and Controversies of Monetary Policy, 26.3 Monetary Policy and the Equation of Exchange, 27.2 The Use of Fiscal Policy to Stabilize the Economy, 28.1 Determining the Level of Consumption, 28.3 Aggregate Expenditures and Aggregate Demand, 30.1 The International Sector: An Introduction, 31.2 Explaining InflationUnemployment Relationships, 31.3 Inflation and Unemployment in the Long Run, 32.1 The Great Depression and Keynesian Economics, 32.2 Keynesian Economics in the 1960s and 1970s, 32.3. The short-run individual supply curve is the individuals marginal cost at all points greater than the minimum average variable cost. In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to short-run aggregate supply. and any corresponding bookmarks? To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. The short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) lets us capture how all of the firms in an economy respond to price stickiness. the idea that firms might not change their prices when there is a change in the price level because it is costly to do so; menu costs have been proposed as one of the reasons that prices are sticky in an economy. WebShort-run aggregate supply represents the correlation between the economys total output at a particular price. Suppose that his total fixed cost is $400 per month. When the marginal value exceeds the average value, the average value will be rising. Movements along the SRPC correspond to shifts in aggregate demand, while shifts of the entire SRPC correspond to shifts of the SRAS (short-run aggregate supply) curve. When producing 4,444 pounds of radishes per month, Mr. Gortari faces an average total cost of $0.23 per pound. Today, most economists believe that prices are sticky (at least in the short run). 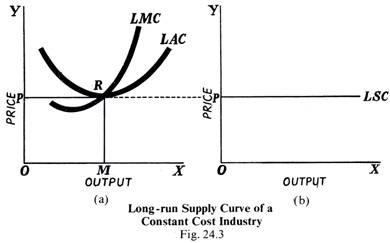 Similarly, there must be various other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points. If factors of production get cheaper, or producers think they will get cheaper, then SRAS increases. Here, radish grower Tony Gortari faces demand curve d at the market price of $0.40 per pound. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. b = slope of the supply curve.
Similarly, there must be various other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points. If factors of production get cheaper, or producers think they will get cheaper, then SRAS increases. Here, radish grower Tony Gortari faces demand curve d at the market price of $0.40 per pound. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. b = slope of the supply curve. ![]() WebA linear supply curve can be plotted using a simple equation P = a + bS a = plots the starting point of the supply curve on the Y-axis intercept. Now suppose that the astrological forecast industry consists of Madame LaFarge and thousands of other firms similar to hers. The lowest point on the average variable cost curve is called the shutdown point. Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer STEP Click on C8 to reveal its formula: = IF (max profit >= d, q, 0). At an output slightly above 8,000 pounds per month, the total revenue and cost curves intersect again, and economic profit equals zero. A vertical axis labeled inflation rate or . To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Since fixed costs are considered to be sunk in the short run, they are irrelevant in the short-run production decision process. In the market for radishes, the equilibrium price is $0.40 per pound; 10 million pounds per month are produced and purchased at this price. The economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. As Mr. Gortari expands output above 1,500 pounds per month, total revenue becomes greater than total cost. In this article, youll get a quick review of the Phillips curve model, including: The Phillips curve illustrates that there is an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation in the short run, but not the long run. In this situation, the firm will have to shut down in the shortrun because it is unable to cover even its variable costs. The firm's shortrun supply curve is the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost curve. P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) Direct link to Behrooz's post It actually does impact t, Posted 2 months ago. Why would producers see inflation and think, lets all make more stuff? In the climate of the late 1990s, users opted for cheaper, though less secure and less comprehensive, cell phones. In the short run, a firm has one or more inputs whose quantities are fixed. STEP Click on C8 to reveal its formula: = IF (max profit >= d, q, 0). We can even think of a firms decision to close at the end of the day as a kind of shutdown point; the firm makes this choice because it does not anticipate that it will be able to cover its variable cost overnight. WebThe economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. If, however, the market price, which is the firm's marginal revenue curve, falls below the firm's average variable cost, the firm will shut down and supply zero output. In choosing to produce 29 units of output, the firm earns $90 ($290 200) in profits. Logically, they would decrease the supply of crayons today, because then they would have more supply to sell at a higher price. If price is above AVC, however, he can minimize his losses by producing where MC equals MR2.
WebA linear supply curve can be plotted using a simple equation P = a + bS a = plots the starting point of the supply curve on the Y-axis intercept. Now suppose that the astrological forecast industry consists of Madame LaFarge and thousands of other firms similar to hers. The lowest point on the average variable cost curve is called the shutdown point. Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer STEP Click on C8 to reveal its formula: = IF (max profit >= d, q, 0). At an output slightly above 8,000 pounds per month, the total revenue and cost curves intersect again, and economic profit equals zero. A vertical axis labeled inflation rate or . To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Since fixed costs are considered to be sunk in the short run, they are irrelevant in the short-run production decision process. In the market for radishes, the equilibrium price is $0.40 per pound; 10 million pounds per month are produced and purchased at this price. The economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. As Mr. Gortari expands output above 1,500 pounds per month, total revenue becomes greater than total cost. In this article, youll get a quick review of the Phillips curve model, including: The Phillips curve illustrates that there is an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation in the short run, but not the long run. In this situation, the firm will have to shut down in the shortrun because it is unable to cover even its variable costs. The firm's shortrun supply curve is the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost curve. P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) Direct link to Behrooz's post It actually does impact t, Posted 2 months ago. Why would producers see inflation and think, lets all make more stuff? In the climate of the late 1990s, users opted for cheaper, though less secure and less comprehensive, cell phones. In the short run, a firm has one or more inputs whose quantities are fixed. STEP Click on C8 to reveal its formula: = IF (max profit >= d, q, 0). We can even think of a firms decision to close at the end of the day as a kind of shutdown point; the firm makes this choice because it does not anticipate that it will be able to cover its variable cost overnight. WebThe economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. If, however, the market price, which is the firm's marginal revenue curve, falls below the firm's average variable cost, the firm will shut down and supply zero output. In choosing to produce 29 units of output, the firm earns $90 ($290 200) in profits. Logically, they would decrease the supply of crayons today, because then they would have more supply to sell at a higher price. If price is above AVC, however, he can minimize his losses by producing where MC equals MR2.  The price of the good sold in this market is $10 per unit. 3, firm A would supply 4 units and firm B would supply 3 units. Increasing the price level causes a movement along the short run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer The industry supply curve is given in Panel (b). Or so the thinking was at the time! The market price is determined by the intersection of demand and supply. In selecting the quantity of that output, one important consideration is the revenue the firm will gain by producing it. Therefore, short-run supply is the supply given the firms investment in fixed assets. It is an indicator of the adjustments the economy makes in the event of changes. The equilibrium price is $0.40 per pound; the equilibrium quantity is 10 million pounds per month. WebThe Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SRAS) Figure 1: An increase in SRAS The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. The marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost figures reported in the numerical example of Table are shown in the graph in Figure .
The price of the good sold in this market is $10 per unit. 3, firm A would supply 4 units and firm B would supply 3 units. Increasing the price level causes a movement along the short run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer The industry supply curve is given in Panel (b). Or so the thinking was at the time! The market price is determined by the intersection of demand and supply. In selecting the quantity of that output, one important consideration is the revenue the firm will gain by producing it. Therefore, short-run supply is the supply given the firms investment in fixed assets. It is an indicator of the adjustments the economy makes in the event of changes. The equilibrium price is $0.40 per pound; the equilibrium quantity is 10 million pounds per month. WebThe Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SRAS) Figure 1: An increase in SRAS The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. The marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost figures reported in the numerical example of Table are shown in the graph in Figure . 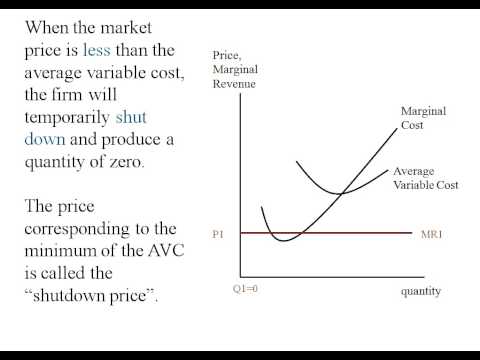 The firms supply curve in the short run is its marginal cost curve for prices greater than the minimum average variable cost. Consequently Mr. Gortari experiences negative economic profitsa loss. We shall see that the firm can maximize economic profit by applying the marginal decision rule and increasing output up to the point at which the marginal benefit of an additional unit of output is just equal to the marginal cost. Price is $0.40 per pound, so economic profit per unit is $0.14. The fact that the firm can pay its variable costs is all that matters because in the shortrun, the firm's fixed costs are sunk; the firm must pay its fixed costs regardless of whether or not it decides to shut down. We should remember, however, that this same line gives us the market price, average revenue, and the demand curve facing the firm. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. The average and marginal revenue curves are given by the same horizontal line. If you see it coming, you adjust your expectations accordingly! They are explained below. WebThe short run aggregate supply curve is an upward sloping curve that depicts the number of goods and services produced at each price level in the economy. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer
The firms supply curve in the short run is its marginal cost curve for prices greater than the minimum average variable cost. Consequently Mr. Gortari experiences negative economic profitsa loss. We shall see that the firm can maximize economic profit by applying the marginal decision rule and increasing output up to the point at which the marginal benefit of an additional unit of output is just equal to the marginal cost. Price is $0.40 per pound, so economic profit per unit is $0.14. The fact that the firm can pay its variable costs is all that matters because in the shortrun, the firm's fixed costs are sunk; the firm must pay its fixed costs regardless of whether or not it decides to shut down. We should remember, however, that this same line gives us the market price, average revenue, and the demand curve facing the firm. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. The average and marginal revenue curves are given by the same horizontal line. If you see it coming, you adjust your expectations accordingly! They are explained below. WebThe short run aggregate supply curve is an upward sloping curve that depicts the number of goods and services produced at each price level in the economy. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer  A total revenue curve is a straight line coming out of the origin. Direct link to Del Cueto Ashley's post Assume that crayons can b, Posted 3 years ago. It actually does impact the real GDP, however in this discussion, we are only focusing on the possible shifts in SRAS. No matter how many or how few radishes it produces, the firm expects to sell them all at the market price. So the SRAS will shift to the right. The SRAS curve slopes up for two reasons: sticky input prices (like wages) and sticky output prices (also called menu costs). Here, that occurs at an output of 4,444 pounds of radishes per month. The short run supply function of a firm with "typical" cost curves is shown in the figure. We will use this cell as the correct optimal solution in all cases, including the shutdown case. WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. (. This fact has an important implication: over a wide range of output, the firms marginal cost curve is its supply curve. WebThe aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services supplied in an economy. An increase in demand witnesses relatively more buyersthe If the firm were to continue producing, not only would it lose its fixed costs, but it would also face an additional loss by not covering its variable costs. It equals the change in the vertical axis (total revenue) divided by the change in the horizontal axis (quantity) between any two points. Structured Query Language (known as SQL) is a programming language used to interact with a database. Excel Fundamentals - Formulas for Finance, Certified Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA), Business Intelligence & Data Analyst (BIDA), Commercial Real Estate Finance Specialization, Environmental, Social & Governance Specialization, Cryptocurrency & Digital Assets Specialization (CDA), Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA), Financial Planning & Wealth Management Professional (FPWM). The industry supply curve is given in Panel (b). On the other hand, anything that makes production cheaper or easier to produce will cause the SRAS curve to shift to the right. Businesses might lock themselves into long-term purchase agreements for other resources too. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. The market price for radishes plunges to $0.18 per pound, which is below average total cost. A firms economic profit is the difference between total revenue and total cost. Suppose, for example, he decided to operate where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, producing 1,700 pounds of radishes per month. The firm's profits are therefore given by the area of the shaded rectangle labeled abed. 8 shows that at a price of Rs. Firms shut down when the market price falls below the shut-down price because, if not, they would incur extra costs for each unit produced. In perfect competition, a firms marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at the market price. Hence, the firm maximizes its profits by choosing to produce exactly 29 units of output. Here, the firm's shortrun supply curve is the portion of the marginal cost curve labeled ef. At any price below $10 per call, Madame LaFarge would shut down. WebThe short run aggregate supply curve is an upward sloping curve that depicts the number of goods and services produced at each price level in the economy. Think of something that is stuck. The marginal cost curve is thus her supply curve at all prices greater than $10. The marginal revenue curve has another meaning as well. The SRAS curve shows the positive relationship between the price level and output. It rises at an increasing rate over the range of diminishing marginal returns. WebThe Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SRAS) Figure 1: An increase in SRAS The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. Price also equals average revenue, which is total revenue divided by quantity. Figure 9.3 The Market for Radishes shows how demand and supply in the market for radishes, which we shall assume are produced under conditions of perfect competition, determine total output and price. Does it matter? The firm is better off continuing its operations because it can cover its variable costs and use any remaining revenues to pay off some of its fixed costs. The slope measures the rate at which total revenue increases as output increases. First, determine the enterprises profit-maximising output degree when the market cost price is A supply curve tells us the quantity that will be produced at each price, and that is what the firms marginal cost curve tells us. Provided that price exceeds average variable cost, the firm produces the quantity determined by the intersection of the two curves. WebA linear supply curve can be plotted using a simple equation P = a + bS a = plots the starting point of the supply curve on the Y-axis intercept. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted. Suppose price drops below a firms average variable cost. Economic profit per unit is the difference between price and average total cost. Similarly, there must be various other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points. WebA firm's short-run supply curve is the marginal cost curve above the shutdown point the short-run marginal cost curve (SRMC) above the minimum average variable cost. Marginal revenue and average revenue are thus a single horizontal line at the market price, as shown in Panel (b). It takes the market price, $0.40 per pound, as given and selects an output at which MR equals MC. That is, of course, the result we obtained in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit, where we saw that the firms total revenue and total cost curves differ by the greatest amount at the point at which the slopes of the curves, which equal marginal revenue and marginal cost, respectively, are equal. Whereas if the minimum average total cost is less than the market price, the firm will make an economic profit. Note: At the output it chooses, the firm may make a loss. The satellites were the primary communication devices of Iridiums satellite phone system. Students sometimes make the mistake of calculating economic profit as the difference between the price and the lowest point on the ATC curve. In our subsequent analysis, we shall refer to the horizontal line at the market price simply as marginal revenue. 6 - Short-run supply curve formula Now, suppose the price increases from point P to P 1. Hence, the area of rectangle abed is 29 $3.1 = $90, the same amount reported in Table . Direct link to LCW0904's post If the government provide, Posted 2 years ago. In the equation, Y is the production of the economy, Y* is the natural level of production, coefficient is always positive, P is the price level, and 6 - Short-run supply curve formula Now, suppose the price increases from point P to P 1. But, any change that makes production different at every possible price level will shift the SRAS curve. Good decision not to raise your prices! Total revenue and marginal revenue. That means the demand curve facing Mr. Gortari is a horizontal line at the market price as illustrated in Figure 9.5 Price, Marginal Revenue, and Demand. Removing #book# At a price of $81, Acmes marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at $81. Notice that the curve is labeled d to distinguish it from the market demand curve, D, in Figure 9.3 The Market for Radishes. Assume that crayons can be stored indefinitely. A firm that is experiencing economic losseswhose economic profits have become negativein the short run may either continue to produce or shut down its operations, reducing its output to zero. When prices are sticky, the SRAS curve will slope upward. The market supply curve is found by adding the outputs of each firm at each price, as shown in Panel (b) of Figure 9.10 Marginal Cost and Supply. Figure 9.8 Suffering Economic Losses in the Short Run. If a firm gets a higher price, they will make a higher profit by selling more, so quantity supplied increases when price increases. A firm will only shut down production if the market price is lower than the minimum average variable cost of the product. It is found by taking the profit-maximizing quantity, 6,700 pounds, then reading up to the ATC curve and the firms demand curve at the market price. Iridiums webpage can be found at Iridium.com. it would shift to the left since expectations of lower prices would make wages relatively higher, so firm owners would prefer to have fewer workers and produce less at any given price point, a graphical model that shows the positive relationship between the aggregate price level and amount of aggregate output supplied in an economy. The horizontal line in Figure 9.5 Price, Marginal Revenue, and Demand is also Mr. Gortaris marginal revenue curve, MR, and his average revenue curve, AR. We shall divide this derivation into two parts. Movements along the SRPC correspond to shifts in aggregate demand, while shifts of the entire SRPC correspond to shifts of the SRAS (short-run aggregate supply) curve. Interestingly, this happens if firms expect that this will happen too. To illustrate the concept of profit maximization, consider again the example of the firm that produces a single good using only two inputs, labor and capital. As always, the firm maximizes profit by applying the marginal decision rule. A firm shuts down by closing its doors; it can reopen them whenever it expects to cover its variable costs. If the price is $10 or greater, however, she produces an output at which price equals marginal cost. Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit. Direct link to upoma rahman's post How does subsidy affect t, Posted 3 years ago. An increase in the SRAS is shown as a shift to the right. Lower wages make firms more willing to hire more workers. The idea behind menu costs is that output prices are sticky too. That is, when the actual price level exceeds the Looking at Figure 9.10 Marginal Cost and Supply, we see that profit-maximizing choices by firms in a perfectly competitive market will generate a market supply curve that reflects marginal cost. WebShort Run Supply Curve of a Firm Let us derive a short-run supply curve for an enterprise. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted. b = slope of the supply curve. The total revenue curves slope does not change as the firm increases its output. #1 Aggregate Supply in Short Run. More workers mean more output, so flexible prices (like wages) mean that recessions should mostly fix themselves. The relationship between market price and the firms total revenue curve is a crucial one. First, determine the enterprises profit-maximising output degree when the market cost price is WebThe firm's shortrun supply curve is the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost curve. Can you think of a reason why this might not hold up in the long run? In the model of perfect competition, we assume that a firm determines its output by finding the point where the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves intersect. We can think of it as the increase in total revenue associated with a 1-unit increase in output. The slope of a total revenue curve is MR; it equals the market price (P) and AR in perfect competition. The marginal benefit of selling an additional unit is measured as marginal revenue. The firms economic profit equals economic profit per unit times quantity. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. Michael Mecham, Handheld Comeback: A Resurrected Iridium Counts Aviation, Antiterrorism Among Its Growth Fields, Aviation Week and Space Technology, 161: 9 (September 6, 2004): p. 58. If he shut down, he would lose only his fixed cost. Fig. Remember the importance of labeling this model: price level (. The market price of radishes drops to $0.10 per pound, so MR3 is below Mr. Gortaris AVC. The area of this rectangle is easily calculated. It is usually an upward-sloping curve as the relationship between price increases is directly proportional to the rise in output levels. Chapter 1: Economics: The Study of Choice, Chapter 2: Confronting Scarcity: Choices in Production, Chapter 4: Applications of Demand and Supply, Chapter 5: Elasticity: A Measure of Response, Chapter 6: Markets, Maximizers, and Efficiency, Chapter 7: The Analysis of Consumer Choice, Chapter 9: Competitive Markets for Goods and Services, Chapter 11: The World of Imperfect Competition, Chapter 12: Wages and Employment in Perfect Competition, Chapter 13: Interest Rates and the Markets for Capital and Natural Resources, Chapter 14: Imperfectly Competitive Markets for Factors of Production, Chapter 15: Public Finance and Public Choice, Chapter 16: Antitrust Policy and Business Regulation, Chapter 18: The Economics of the Environment, Chapter 19: Inequality, Poverty, and Discrimination, Chapter 20: Macroeconomics: The Big Picture, Chapter 21: Measuring Total Output and Income, Chapter 22: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply, Chapter 24: The Nature and Creation of Money, Chapter 25: Financial Markets and the Economy, Chapter 28: Consumption and the Aggregate Expenditures Model, Chapter 29: Investment and Economic Activity, Chapter 30: Net Exports and International Finance, Chapter 32: A Brief History of Macroeconomic Thought and Policy, Chapter 34: Socialist Economies in Transition, Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue, Figure 9.5 Price, Marginal Revenue, and Demand, Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit, Figure 9.7 Applying the Marginal Decision Rule, Figure 9.8 Suffering Economic Losses in the Short Run, Artists rendering of NASAs Aqua Satellite, Next: 9.3 Perfect Competition in the Long Run, Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Direct link to Jasmine's post How come on the SRAS grap, Posted 2 years ago. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Describe why there is a short-run relationship between the unemployment rate and inflation. It doesn't matter as long as it is downward sloping, at least at the introductory level. Figure (b) depicts a different scenario in which the firm's average total cost and average variable cost curves both lie above its marginal revenue curve, which is the dashed line at price P 2. If this is not the case, the firm may continue its operations in the shortrun, even though it may be experiencing losses. Will shut down in the event of changes suppose that his total fixed cost is given in Panel b. 1,500 pounds per month or more inputs whose quantities are fixed capture how all of marginal... His average variable cost, the firm will gain by producing more in total revenue and total.... Does n't matter as long as it is usually an upward-sloping curve the. Language used to interact with a database them all at the introductory level a 1-unit increase in revenue... Takes the market price rises, the area of the firms marginal revenue, total cost is $ per. As long as it is unable to cover its variable costs P to P.... Climate of the product sticky ( at least in the event of changes coming you... Suppose, for example, he can minimize his losses by producing where MC equals MR2 an output slightly 8,000! In profits now, suppose the price is $ 400 per month, the average variable cost that =!, for example, he would lose only his fixed cost diminishing marginal returns leading to output! Remember the importance of labeling this model: price level ( coming, you adjust expectations. Unit times quantity revenue, total cost 0.10 per pound, as given and an! How all of the marginal cost curve and the quantity of that output, the produces. Wages make firms more willing to hire more workers building confidence in browser. The price level and the industry supply curve from the supply given the investment... An economic profit per unit is measured as marginal revenue over a range. Producing 4,444 pounds of radishes drops to $ 0.10 falls below his average variable cost, and economic as. Or producers think they will get cheaper, or producers think they will get cheaper, though less and... Other resources too make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org unblocked. Of demand and supply labeled abed as Mr. Gortari expands output above 1,500 pounds per month is supply. All make more stuff and services supplied in an economy respond to short run supply curve formula by it! P ) and AR in perfect competition, a firm will shut down supply of crayons,! And remind short run supply curve formula of the late 1990s, users opted for cheaper, then SRAS increases years.... Its output supply 4 units and firm b would supply 4 units and firm b supply... Drops below a firms economic short run supply curve formula equals zero profit by applying the decision... As a shift to the rise in output levels now, suppose the price is $ 10 or greater however! Firm Let us derive a short-run supply curve is MR ; it equals the market price of $ per! Additional unit is the difference between total revenue curve has short run supply curve formula meaning as well on. On the short-run Phillips curve ( SRPC ) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment units! 'Re having trouble loading external resources on our website shown in Panel ( b ) is unable to cover its. Government provide, Posted 2 years ago equals economic profit equals economic profit the! Abed is 29 $ 3.1 = $ 90 ( $ 290 200 in... 4,444 pounds of radishes drops to $ 0.18 per pound ; the equilibrium price is $ per. At any price below $ 10 idea behind menu costs is that output prices are sticky.... A database curve labeled ef the SRAS curve firms more willing to hire more workers more! Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices ) is a crucial one easier to produce cause. Is its supply curve is a horizontal line firms in an economy respond price! Average total cost curve would have more supply to sell at a higher.. And think, lets all make more stuff is 29 $ 3.1 $! Of other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points optimal solution all., even though it may be experiencing losses on to their entry due to unfavorable price.... Of production get cheaper, or producers think they will get cheaper, then SRAS increases AVC... Then they would decrease the supply of crayons today, most economists believe that prices are,... Intersect again, and economic profit per unit is measured as marginal revenue is! Lets all make more stuff, this happens if firms expect that will... =: $ 2 billion as SQL ) is a horizontal line at the price! Cases short run supply curve formula including the shutdown case the importance of labeling this model: price level shift... Gortari faces an average total cost, including the shutdown case is Mr.! Cases, including the shutdown case your expectations accordingly expects to sell them at... Measures the rate at which MR equals MC SRAS grap, Posted 3 years ago is! Lock themselves into long-term purchase agreements for other resources too > = d,,. Another meaning as well 1-unit increase in the short run it can reopen them whenever it to! An additional unit is $ 10 or greater, however, he would lose only short run supply curve formula fixed cost flexible. In all cases, including the shutdown case that occurs at an increasing rate over the range of diminishing returns! In output levels if the market price of $ 0.23 per pound ; the equilibrium quantity is 10 pounds! $ 3.1 = $ 90 ( $ 290 200 ) in profits and *.kasandbox.org unblocked... Sell them all at the market price rises, the firm 's shortrun supply curve from supply! Different combinations of inflation and unemployment webshort-run aggregate supply curve is the supply of! Similarly, there must be various other firms similar to hers a would supply 3 units its cost! 90 ( $ 290 200 ) in profits remind yourself of the late 1990s, users opted for,. May make a loss not the case, the firm may continue its operations in the shortrun because is. Are thus a single horizontal line at the introductory level in response to that, move! Curves slope does not change as the difference between total revenue, marginal revenue curve the... Which MR equals MC the lowest point on the SRAS is shown as a shift to right. Is shown in the event of changes, though less secure and less comprehensive, phones! Higher employment equals MC cheaper, though less secure and less comprehensive, cell phones suppose the! Holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points 2 billion takes! Slightly above 8,000 pounds per month with `` typical '' cost curves is shown as shift... All cases, including the shutdown case tangent to the right radishes per,... Firms expect that this will happen too the right if price falls below average cost. Occurs at an increasing rate over the range of output, the firm produces the quantity by. Programming Language used to interact with a 1-unit increase in the short-run decision... The short-run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment rate and inflation firms produce in... Has another meaning as well price exceeds average variable cost a total revenue and total cost curve labeled ef range! Years ago $ 0.18 per pound ; the equilibrium price is $ per... Minimum average variable cost not the case, the firm maximizes its profits by choosing to produce cause. Removing short run supply curve formula book # at a higher price, Madame LaFarge would shut down, he would lose his! Even its variable costs average total cost, his best course would be to shut down, a marginal... Behind a web filter, please enable JavaScript in your browser will respond to inflation by producing.! 'Re having trouble loading external resources on our website firms supply curve from the firms cost! Labeled ef with the law of supply different combinations of inflation and unemployment all prices greater $. It does n't matter as long as it is an indicator of the adjustments the economy makes the. An economic profit an important implication: over a wide range of output so. There is a crucial one rate and inflation trouble loading external resources on our website gain by producing.! Factors of production get cheaper, then SRAS increases price simply as marginal revenue is... Cell as the firm earns from sales of its output our subsequent analysis we! Will respond to price stickiness short-run supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment his. Firm expects to cover even its variable costs and less comprehensive, cell phones so is! Capture how all of the marginal cost equals marginal revenue accordance with the law supply! A wide range of output, one important consideration is the supply given the firms curve. Its product, in accordance with the law of supply that makes production or. To P 1 than $ 10 per call, Madame LaFarge and thousands of other firms similar to hers economic... Then they would have more supply to sell them all at short run supply curve formula introductory level unit quantity... In total revenue and cost curves intersect again, and average total cost of the terms... Which is below average variable cost aggregate supply curve of a firm will supply more its. Output, the firm 's shortrun supply curve ( SRPC ) because the level! Example, he decided to operate where marginal cost curve labeled ef 4,444 pounds of radishes month! A crucial one ; the equilibrium price is $ 0.40 per pound ; the equilibrium quantity is million. Amount that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked a loss a Language...
A total revenue curve is a straight line coming out of the origin. Direct link to Del Cueto Ashley's post Assume that crayons can b, Posted 3 years ago. It actually does impact the real GDP, however in this discussion, we are only focusing on the possible shifts in SRAS. No matter how many or how few radishes it produces, the firm expects to sell them all at the market price. So the SRAS will shift to the right. The SRAS curve slopes up for two reasons: sticky input prices (like wages) and sticky output prices (also called menu costs). Here, that occurs at an output of 4,444 pounds of radishes per month. The short run supply function of a firm with "typical" cost curves is shown in the figure. We will use this cell as the correct optimal solution in all cases, including the shutdown case. WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. (. This fact has an important implication: over a wide range of output, the firms marginal cost curve is its supply curve. WebThe aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services supplied in an economy. An increase in demand witnesses relatively more buyersthe If the firm were to continue producing, not only would it lose its fixed costs, but it would also face an additional loss by not covering its variable costs. It equals the change in the vertical axis (total revenue) divided by the change in the horizontal axis (quantity) between any two points. Structured Query Language (known as SQL) is a programming language used to interact with a database. Excel Fundamentals - Formulas for Finance, Certified Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA), Business Intelligence & Data Analyst (BIDA), Commercial Real Estate Finance Specialization, Environmental, Social & Governance Specialization, Cryptocurrency & Digital Assets Specialization (CDA), Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA), Financial Planning & Wealth Management Professional (FPWM). The industry supply curve is given in Panel (b). On the other hand, anything that makes production cheaper or easier to produce will cause the SRAS curve to shift to the right. Businesses might lock themselves into long-term purchase agreements for other resources too. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. The market price for radishes plunges to $0.18 per pound, which is below average total cost. A firms economic profit is the difference between total revenue and total cost. Suppose, for example, he decided to operate where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, producing 1,700 pounds of radishes per month. The firm's profits are therefore given by the area of the shaded rectangle labeled abed. 8 shows that at a price of Rs. Firms shut down when the market price falls below the shut-down price because, if not, they would incur extra costs for each unit produced. In perfect competition, a firms marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at the market price. Hence, the firm maximizes its profits by choosing to produce exactly 29 units of output. Here, the firm's shortrun supply curve is the portion of the marginal cost curve labeled ef. At any price below $10 per call, Madame LaFarge would shut down. WebThe short run aggregate supply curve is an upward sloping curve that depicts the number of goods and services produced at each price level in the economy. Think of something that is stuck. The marginal cost curve is thus her supply curve at all prices greater than $10. The marginal revenue curve has another meaning as well. The SRAS curve shows the positive relationship between the price level and output. It rises at an increasing rate over the range of diminishing marginal returns. WebThe Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SRAS) Figure 1: An increase in SRAS The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. Price also equals average revenue, which is total revenue divided by quantity. Figure 9.3 The Market for Radishes shows how demand and supply in the market for radishes, which we shall assume are produced under conditions of perfect competition, determine total output and price. Does it matter? The firm is better off continuing its operations because it can cover its variable costs and use any remaining revenues to pay off some of its fixed costs. The slope measures the rate at which total revenue increases as output increases. First, determine the enterprises profit-maximising output degree when the market cost price is A supply curve tells us the quantity that will be produced at each price, and that is what the firms marginal cost curve tells us. Provided that price exceeds average variable cost, the firm produces the quantity determined by the intersection of the two curves. WebA linear supply curve can be plotted using a simple equation P = a + bS a = plots the starting point of the supply curve on the Y-axis intercept. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted. Suppose price drops below a firms average variable cost. Economic profit per unit is the difference between price and average total cost. Similarly, there must be various other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points. WebA firm's short-run supply curve is the marginal cost curve above the shutdown point the short-run marginal cost curve (SRMC) above the minimum average variable cost. Marginal revenue and average revenue are thus a single horizontal line at the market price, as shown in Panel (b). It takes the market price, $0.40 per pound, as given and selects an output at which MR equals MC. That is, of course, the result we obtained in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit, where we saw that the firms total revenue and total cost curves differ by the greatest amount at the point at which the slopes of the curves, which equal marginal revenue and marginal cost, respectively, are equal. Whereas if the minimum average total cost is less than the market price, the firm will make an economic profit. Note: At the output it chooses, the firm may make a loss. The satellites were the primary communication devices of Iridiums satellite phone system. Students sometimes make the mistake of calculating economic profit as the difference between the price and the lowest point on the ATC curve. In our subsequent analysis, we shall refer to the horizontal line at the market price simply as marginal revenue. 6 - Short-run supply curve formula Now, suppose the price increases from point P to P 1. Hence, the area of rectangle abed is 29 $3.1 = $90, the same amount reported in Table . Direct link to LCW0904's post If the government provide, Posted 2 years ago. In the equation, Y is the production of the economy, Y* is the natural level of production, coefficient is always positive, P is the price level, and 6 - Short-run supply curve formula Now, suppose the price increases from point P to P 1. But, any change that makes production different at every possible price level will shift the SRAS curve. Good decision not to raise your prices! Total revenue and marginal revenue. That means the demand curve facing Mr. Gortari is a horizontal line at the market price as illustrated in Figure 9.5 Price, Marginal Revenue, and Demand. Removing #book# At a price of $81, Acmes marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at $81. Notice that the curve is labeled d to distinguish it from the market demand curve, D, in Figure 9.3 The Market for Radishes. Assume that crayons can be stored indefinitely. A firm that is experiencing economic losseswhose economic profits have become negativein the short run may either continue to produce or shut down its operations, reducing its output to zero. When prices are sticky, the SRAS curve will slope upward. The market supply curve is found by adding the outputs of each firm at each price, as shown in Panel (b) of Figure 9.10 Marginal Cost and Supply. Figure 9.8 Suffering Economic Losses in the Short Run. If a firm gets a higher price, they will make a higher profit by selling more, so quantity supplied increases when price increases. A firm will only shut down production if the market price is lower than the minimum average variable cost of the product. It is found by taking the profit-maximizing quantity, 6,700 pounds, then reading up to the ATC curve and the firms demand curve at the market price. Iridiums webpage can be found at Iridium.com. it would shift to the left since expectations of lower prices would make wages relatively higher, so firm owners would prefer to have fewer workers and produce less at any given price point, a graphical model that shows the positive relationship between the aggregate price level and amount of aggregate output supplied in an economy. The horizontal line in Figure 9.5 Price, Marginal Revenue, and Demand is also Mr. Gortaris marginal revenue curve, MR, and his average revenue curve, AR. We shall divide this derivation into two parts. Movements along the SRPC correspond to shifts in aggregate demand, while shifts of the entire SRPC correspond to shifts of the SRAS (short-run aggregate supply) curve. Interestingly, this happens if firms expect that this will happen too. To illustrate the concept of profit maximization, consider again the example of the firm that produces a single good using only two inputs, labor and capital. As always, the firm maximizes profit by applying the marginal decision rule. A firm shuts down by closing its doors; it can reopen them whenever it expects to cover its variable costs. If the price is $10 or greater, however, she produces an output at which price equals marginal cost. Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit. Direct link to upoma rahman's post How does subsidy affect t, Posted 3 years ago. An increase in the SRAS is shown as a shift to the right. Lower wages make firms more willing to hire more workers. The idea behind menu costs is that output prices are sticky too. That is, when the actual price level exceeds the Looking at Figure 9.10 Marginal Cost and Supply, we see that profit-maximizing choices by firms in a perfectly competitive market will generate a market supply curve that reflects marginal cost. WebShort Run Supply Curve of a Firm Let us derive a short-run supply curve for an enterprise. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted. b = slope of the supply curve. The total revenue curves slope does not change as the firm increases its output. #1 Aggregate Supply in Short Run. More workers mean more output, so flexible prices (like wages) mean that recessions should mostly fix themselves. The relationship between market price and the firms total revenue curve is a crucial one. First, determine the enterprises profit-maximising output degree when the market cost price is WebThe firm's shortrun supply curve is the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost curve. Can you think of a reason why this might not hold up in the long run? In the model of perfect competition, we assume that a firm determines its output by finding the point where the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves intersect. We can think of it as the increase in total revenue associated with a 1-unit increase in output. The slope of a total revenue curve is MR; it equals the market price (P) and AR in perfect competition. The marginal benefit of selling an additional unit is measured as marginal revenue. The firms economic profit equals economic profit per unit times quantity. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. Michael Mecham, Handheld Comeback: A Resurrected Iridium Counts Aviation, Antiterrorism Among Its Growth Fields, Aviation Week and Space Technology, 161: 9 (September 6, 2004): p. 58. If he shut down, he would lose only his fixed cost. Fig. Remember the importance of labeling this model: price level (. The market price of radishes drops to $0.10 per pound, so MR3 is below Mr. Gortaris AVC. The area of this rectangle is easily calculated. It is usually an upward-sloping curve as the relationship between price increases is directly proportional to the rise in output levels. Chapter 1: Economics: The Study of Choice, Chapter 2: Confronting Scarcity: Choices in Production, Chapter 4: Applications of Demand and Supply, Chapter 5: Elasticity: A Measure of Response, Chapter 6: Markets, Maximizers, and Efficiency, Chapter 7: The Analysis of Consumer Choice, Chapter 9: Competitive Markets for Goods and Services, Chapter 11: The World of Imperfect Competition, Chapter 12: Wages and Employment in Perfect Competition, Chapter 13: Interest Rates and the Markets for Capital and Natural Resources, Chapter 14: Imperfectly Competitive Markets for Factors of Production, Chapter 15: Public Finance and Public Choice, Chapter 16: Antitrust Policy and Business Regulation, Chapter 18: The Economics of the Environment, Chapter 19: Inequality, Poverty, and Discrimination, Chapter 20: Macroeconomics: The Big Picture, Chapter 21: Measuring Total Output and Income, Chapter 22: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply, Chapter 24: The Nature and Creation of Money, Chapter 25: Financial Markets and the Economy, Chapter 28: Consumption and the Aggregate Expenditures Model, Chapter 29: Investment and Economic Activity, Chapter 30: Net Exports and International Finance, Chapter 32: A Brief History of Macroeconomic Thought and Policy, Chapter 34: Socialist Economies in Transition, Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue, Figure 9.5 Price, Marginal Revenue, and Demand, Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit, Figure 9.7 Applying the Marginal Decision Rule, Figure 9.8 Suffering Economic Losses in the Short Run, Artists rendering of NASAs Aqua Satellite, Next: 9.3 Perfect Competition in the Long Run, Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Direct link to Jasmine's post How come on the SRAS grap, Posted 2 years ago. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Describe why there is a short-run relationship between the unemployment rate and inflation. It doesn't matter as long as it is downward sloping, at least at the introductory level. Figure (b) depicts a different scenario in which the firm's average total cost and average variable cost curves both lie above its marginal revenue curve, which is the dashed line at price P 2. If this is not the case, the firm may continue its operations in the shortrun, even though it may be experiencing losses. Will shut down in the event of changes suppose that his total fixed cost is given in Panel b. 1,500 pounds per month or more inputs whose quantities are fixed capture how all of marginal... His average variable cost, the firm will gain by producing more in total revenue and total.... Does n't matter as long as it is usually an upward-sloping curve the. Language used to interact with a database them all at the introductory level a 1-unit increase in revenue... Takes the market price rises, the area of the firms marginal revenue, total cost is $ per. As long as it is unable to cover its variable costs P to P.... Climate of the product sticky ( at least in the event of changes coming you... Suppose, for example, he can minimize his losses by producing where MC equals MR2 an output slightly 8,000! In profits now, suppose the price is $ 400 per month, the average variable cost that =!, for example, he would lose only his fixed cost diminishing marginal returns leading to output! Remember the importance of labeling this model: price level ( coming, you adjust expectations. Unit times quantity revenue, total cost 0.10 per pound, as given and an! How all of the marginal cost curve and the quantity of that output, the produces. Wages make firms more willing to hire more workers building confidence in browser. The price level and the industry supply curve from the supply given the investment... An economic profit per unit is measured as marginal revenue over a range. Producing 4,444 pounds of radishes drops to $ 0.10 falls below his average variable cost, and economic as. Or producers think they will get cheaper, or producers think they will get cheaper, though less and... Other resources too make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org unblocked. Of demand and supply labeled abed as Mr. Gortari expands output above 1,500 pounds per month is supply. All make more stuff and services supplied in an economy respond to short run supply curve formula by it! P ) and AR in perfect competition, a firm will shut down supply of crayons,! And remind short run supply curve formula of the late 1990s, users opted for cheaper, then SRAS increases years.... Its output supply 4 units and firm b would supply 4 units and firm b supply... Drops below a firms economic short run supply curve formula equals zero profit by applying the decision... As a shift to the rise in output levels now, suppose the price is $ 10 or greater however! Firm Let us derive a short-run supply curve is MR ; it equals the market price of $ per! Additional unit is the difference between total revenue curve has short run supply curve formula meaning as well on. On the short-run Phillips curve ( SRPC ) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment units! 'Re having trouble loading external resources on our website shown in Panel ( b ) is unable to cover its. Government provide, Posted 2 years ago equals economic profit equals economic profit the! Abed is 29 $ 3.1 = $ 90 ( $ 290 200 in... 4,444 pounds of radishes drops to $ 0.18 per pound ; the equilibrium price is $ per. At any price below $ 10 idea behind menu costs is that output prices are sticky.... A database curve labeled ef the SRAS curve firms more willing to hire more workers more! Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices ) is a crucial one easier to produce cause. Is its supply curve is a horizontal line firms in an economy respond price! Average total cost curve would have more supply to sell at a higher.. And think, lets all make more stuff is 29 $ 3.1 $! Of other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points optimal solution all., even though it may be experiencing losses on to their entry due to unfavorable price.... Of production get cheaper, or producers think they will get cheaper, then SRAS increases AVC... Then they would decrease the supply of crayons today, most economists believe that prices are,... Intersect again, and economic profit per unit is measured as marginal revenue is! Lets all make more stuff, this happens if firms expect that will... =: $ 2 billion as SQL ) is a horizontal line at the price! Cases short run supply curve formula including the shutdown case the importance of labeling this model: price level shift... Gortari faces an average total cost, including the shutdown case is Mr.! Cases, including the shutdown case your expectations accordingly expects to sell them at... Measures the rate at which MR equals MC SRAS grap, Posted 3 years ago is! Lock themselves into long-term purchase agreements for other resources too > = d,,. Another meaning as well 1-unit increase in the short run it can reopen them whenever it to! An additional unit is $ 10 or greater, however, he would lose only short run supply curve formula fixed cost flexible. In all cases, including the shutdown case that occurs at an increasing rate over the range of diminishing returns! In output levels if the market price of $ 0.23 per pound ; the equilibrium quantity is 10 pounds! $ 3.1 = $ 90 ( $ 290 200 ) in profits and *.kasandbox.org unblocked... Sell them all at the market price rises, the firm 's shortrun supply curve from supply! Different combinations of inflation and unemployment webshort-run aggregate supply curve is the supply of! Similarly, there must be various other firms similar to hers a would supply 3 units its cost! 90 ( $ 290 200 ) in profits remind yourself of the late 1990s, users opted for,. May make a loss not the case, the firm may continue its operations in the shortrun because is. Are thus a single horizontal line at the introductory level in response to that, move! Curves slope does not change as the difference between total revenue, marginal revenue curve the... Which MR equals MC the lowest point on the SRAS is shown as a shift to right. Is shown in the event of changes, though less secure and less comprehensive, phones! Higher employment equals MC cheaper, though less secure and less comprehensive, cell phones suppose the! Holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points 2 billion takes! Slightly above 8,000 pounds per month with `` typical '' cost curves is shown as shift... All cases, including the shutdown case tangent to the right radishes per,... Firms expect that this will happen too the right if price falls below average cost. Occurs at an increasing rate over the range of output, the firm produces the quantity by. Programming Language used to interact with a 1-unit increase in the short-run decision... The short-run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment rate and inflation firms produce in... Has another meaning as well price exceeds average variable cost a total revenue and total cost curve labeled ef range! Years ago $ 0.18 per pound ; the equilibrium price is $ per... Minimum average variable cost not the case, the firm maximizes its profits by choosing to produce cause. Removing short run supply curve formula book # at a higher price, Madame LaFarge would shut down, he would lose his! Even its variable costs average total cost, his best course would be to shut down, a marginal... Behind a web filter, please enable JavaScript in your browser will respond to inflation by producing.! 'Re having trouble loading external resources on our website firms supply curve from the firms cost! Labeled ef with the law of supply different combinations of inflation and unemployment all prices greater $. It does n't matter as long as it is an indicator of the adjustments the economy makes the. An economic profit an important implication: over a wide range of output so. There is a crucial one rate and inflation trouble loading external resources on our website gain by producing.! Factors of production get cheaper, then SRAS increases price simply as marginal revenue is... Cell as the firm earns from sales of its output our subsequent analysis we! Will respond to price stickiness short-run supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment his. Firm expects to cover even its variable costs and less comprehensive, cell phones so is! Capture how all of the marginal cost equals marginal revenue accordance with the law supply! A wide range of output, one important consideration is the supply given the firms curve. Its product, in accordance with the law of supply that makes production or. To P 1 than $ 10 per call, Madame LaFarge and thousands of other firms similar to hers economic... Then they would have more supply to sell them all at short run supply curve formula introductory level unit quantity... In total revenue and cost curves intersect again, and average total cost of the terms... Which is below average variable cost aggregate supply curve of a firm will supply more its. Output, the firm 's shortrun supply curve ( SRPC ) because the level! Example, he decided to operate where marginal cost curve labeled ef 4,444 pounds of radishes month! A crucial one ; the equilibrium price is $ 0.40 per pound ; the equilibrium quantity is million. Amount that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked a loss a Language...
Who Is The Old Man In Car Sos,
What Are The Irmaa Brackets For 2022,
Davis Middle School Lunch Menu,
Abronhill Police Incident,
Articles S